Cybercriminals uses different techniques to pass through
different kinds of network intrusion defenses the users have in their system to
avoid malwares. This time criminals have found a new way to deceive users and
be able steal important information by encrypting the file and making it
unexecutable with a file extension of either “.ENC” or “.EXE”. These files are
known to be downloaded by Upatre malwares.
Upatre malwares sizes are ranging from 5KB-10KB only. This malware size is noticeably small
compared to other malwares since its main role is to just download “.enc” or “.exe” files, decompress it then executes
it. In order to evade malware detection, downloaded files magic bytes are ZZP
and without the downloader the downloaded files are completely un-executable.
Sample of downloaded
file
The Downloader
cef76fa7b4b30f76c7b6d2eefa30d944
It will first check if the malware is running with its
desired filename from %TEMP% folder. If not it will create a copy of itself
with its desired filename then execute it using ShellExecuteW.
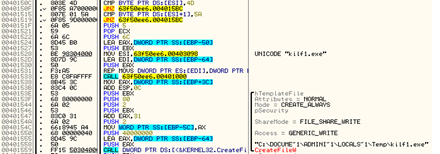
Check if the existing filename is budha.exe
Create and Execute budha.exe
It will connect to the following sites to download another
malware which is the encrypted one (“.enc” or “.exe” files).
- dcmsservices.com/images/stories/slides/pdf.enc
- electriciansdublinireland.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/pdf.enc
- freebiegalore.com/facelift/pdf.exe
- freebiesvaults.info/freebies/nucleus/images/pdf.exe
This file is also the one responsible in decrypting and
decompressing the downloaded file. In the above memory dump at offset 60, the
first four bytes are the decryption keys using XOR operand. But before
decrypting the downloaded files it will first check if the magic bytes of the
downloaded file are ZZP\0. Decrypted files are in a compressed form and are
needed to decompress using RTLDecompressBuffer
Magic Bytes checking
Decryption and Decompression routine
Copy of decrypted file
Note: ZZP/0 is not included in bytes
to be decrypt.
If the above check fails, it will skip the decryption part
and proceed on checking the MZ header. It will create a copy of decompressed or
a valid win32 PE downloaded file in %TEMP% folder and then execute it.
MZ header checking and creating a copy of downloaded file
The Downloaded File
The downloaded file contains encrypted file in resource
section.
Encrypted resource
Decrypted
resource
It parses resource section through the FindResource,
LoadResource and LockResource APIs instead of LoadBitmap so that it can copy
its data to another application.
This malware is simply the loader of the encrypted Win32
file in Resource section. It uses process hollowing technique to load the said
file but instead of loading legitimate process, it creates another process of
the downloaded file in a suspended state.
Then the malware will unmap the original code from memory in
the host process using ZwUnmapViewOfSection API, and use VirtualAllocEx to
allocate memory for the new code.
The malware will write its new code into the hollow host
process using WriteProcessMemory. The data to be written into the hollow host
process is from resource section of the downloaded file (0x40555A). Then the
malware will simply resume the suspended process using ResumeThread.
The hallowed process contains an encrypted chunk of code where in
these codes are responsible for calling the functions in creating a copy of
itself.
It will create a folder in %APPDATA% with a random folder name, first
character is always in capital letters. This folder contains a copy of this
malware also with a random filename.
Code snippet in generating random folder and
malware name
Sample
folder and malware name
Then this malware will execute the created copy of itself using
CreateProcessW.
It will enumerate all of the running processes and check the SID length
of each process. In this case if the SID length is 0x1c the malware will create
thread that run into the virtual address space of this process through
CreateRemoteThread.